postgresql数据库如何实现字符串分割字段转列表查询
在数据查询中,有一张a表存有另一张b表的id并以‘,’隔开
如:
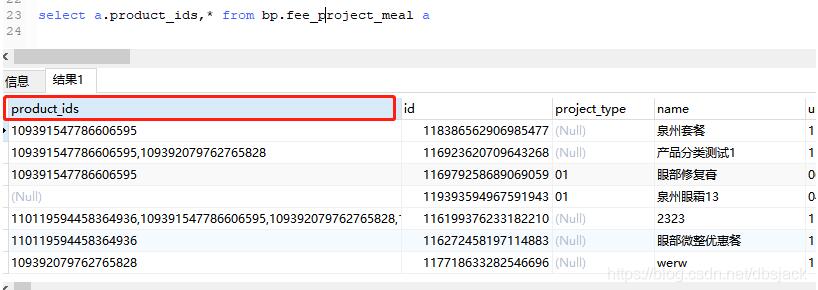
假设现在要关联查询关于 b表的一些信息,怎么办。
分割查询:字符串转列表函数 :regexp_split_to_table()
select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from fee_project_meal where id = 116199376233182210 ), ‘,’)
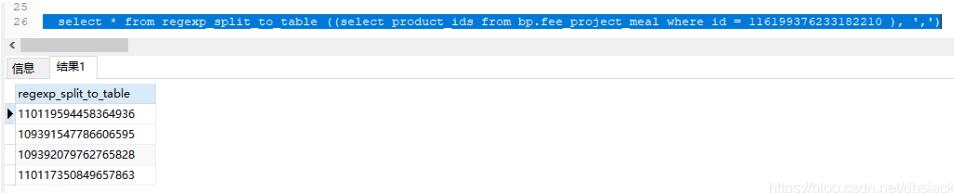
查询后,字符串就变成了列表,然后你就可以根据这个列表去找b表的相关信息了。
select *
from pm.product
where id::text in
(select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from bp.fee_project_meal where id = 116199376233182210 ), ‘,’))
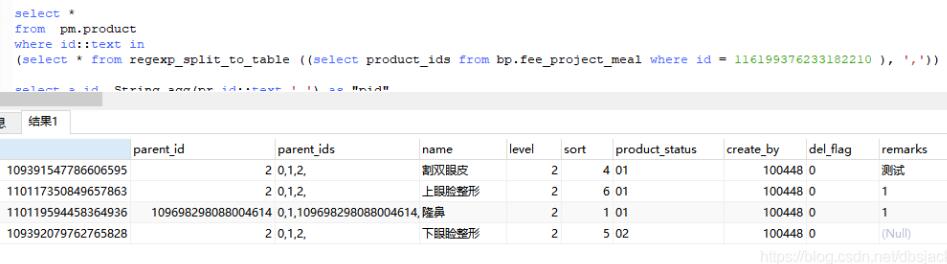
首先数据验证是正确的,说明sql没有问题,接下来就是一起关联查询了
1.因为这个a表与b表是一对多的关系,所以我们先关联出多条。
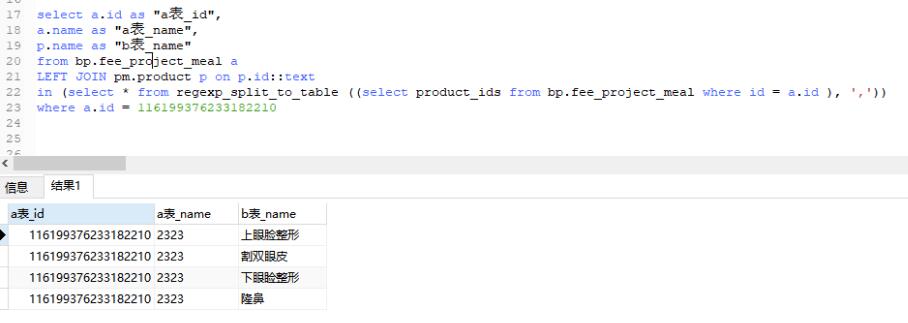
select a.id as “a表_id”,
a.name as “a表_name”,
p.name as “b表_name”
from bp.fee_project_meal a
LEFT JOIN pm.product p on p.id::text
in (select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from bp.fee_project_meal where id = a.id ), ‘,’))
where a.id = 116199376233182210
2.还有一种就是 我只要查出a表的数据,b表的数据中某些字段做未拼接的形式存在,也就是说 现在要查出a表的数据
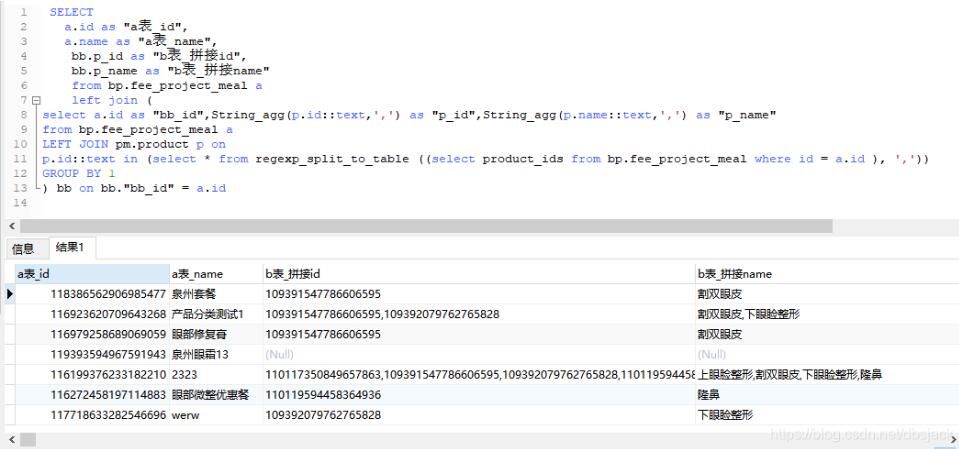
SELECT
a.id as “a表_id”,
a.name as “a表_name”,
bb.p_id as “b表_拼接id”,
bb.p_name as “b表_拼接name”
from bp.fee_project_meal a
left join (
select a.id as “bb_id”,String_agg(p.id::text,’,’) as “p_id”,String_agg(p.name::text,’,’) as “p_name”
from bp.fee_project_meal a
LEFT JOIN pm.product p on
p.id::text in (select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from bp.fee_project_meal where id = a.id ), ‘,’))
GROUP BY 1
) bb on bb.”bb_id” = a.id
在数据查询中,有一张a表存有另一张b表的id并以‘,’隔开
如:

假设现在要关联查询关于 b表的一些信息,怎么办。
分割查询:字符串转列表函数 :regexp_split_to_table()
select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from fee_project_meal where id = 116199376233182210 ), ‘,’)

查询后,字符串就变成了列表,然后你就可以根据这个列表去找b表的相关信息了。
select *
from pm.product
where id::text in
(select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from bp.fee_project_meal where id = 116199376233182210 ), ‘,’))

首先数据验证是正确的,说明sql没有问题,接下来就是一起关联查询了
1.因为这个a表与b表是一对多的关系,所以我们先关联出多条。
select a.id as “a表_id”,
a.name as “a表_name”,
p.name as “b表_name”
from bp.fee_project_meal a
LEFT JOIN pm.product p on p.id::text
in (select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from bp.fee_project_meal where id = a.id ), ‘,’))
where a.id = 116199376233182210

2.还有一种就是 我只要查出a表的数据,b表的数据中某些字段做未拼接的形式存在,也就是说 现在要查出a表的数据
SELECT
a.id as “a表_id”,
a.name as “a表_name”,
bb.p_id as “b表_拼接id”,
bb.p_name as “b表_拼接name”
from bp.fee_project_meal a
left join (
select a.id as “bb_id”,String_agg(p.id::text,’,’) as “p_id”,String_agg(p.name::text,’,’) as “p_name”
from bp.fee_project_meal a
LEFT JOIN pm.product p on
p.id::text in (select * from regexp_split_to_table ((select product_ids from bp.fee_project_meal where id = a.id ), ‘,’))
GROUP BY 1
) bb on bb.”bb_id” = a.id

以上就是,字符串字段的拆解查询。
补充:pgsql 查询字段中根据逗号分隔的字符串的的 个数
select length(translate(column,’,’||column,’,’))+1 from table
参见:
1.translate 与replace类似是替换函数,但translate是一次替换多个单个的字符。
2.基本用法,字符对应替换。
例子:
select translate(‘1234567′,’123′ ,’abc’) from dual ;–1替换为a,2替换为b,3替换为c
结果:abc4567 。
3.如果 没有对应字符则替换为null;
select translate(‘1234567′,’123′ ,’ab’) from dual;–3替换为null;
结果:ab4567.
4.如果对应字符过多,不影响
select translate(‘1234567′,’123′ ,’abccd’) from dual;
结果:abc4567
5.如果替换字符整个为空字符 ,则直接返回null
select translate(‘1234567′,’123’ ,”) from dual;
结果:null;
6.如果想筛掉对应字符,应传入一个不相关字符,同时替换字符也加一个相同字符;
select translate(‘1234567′,’&123′ ,’&’) from dual;
结果:4567;
7.如果相同字符对应多个字符,按第一个;
select translate(‘12334567′,’1233′ ,‘abcd’) from dual;
结果:abcc4567;
8.如果想保留某些特定字符筛选掉其他的,比如筛掉汉字保留数字
先把数字筛选掉,
select translate(‘你师看了3三楼2的6开8发’,’#0123456789′ ,’#’) from dual
再用筛选出的汉字去筛选原来的语句留下数字,
select translate(‘你师看了3三楼2的6开8发’,’#’||translate(‘你师看了3三楼2的6开8发’,’#0123456789′ ,’#’),’#’) from dual;
结果:3268;
9.还有其他灵活用法,比如我可以判断两个字符串如果:字符串都是数字字符,然后数字字符的顺序不同,且每个字符只出现一次,
我可以判断他们包含的数字是不是完全一致;
比如比较123 和132;
select 1 from dual where
translate(‘0123456789′,’123′ ,’aaaaaaaaaa’) =translate(‘0123456789′,’132′ ,’aaaaaaaaaa’)
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。

